Structures of Folates
The vitamers of the folate group display a high variety of different structures.
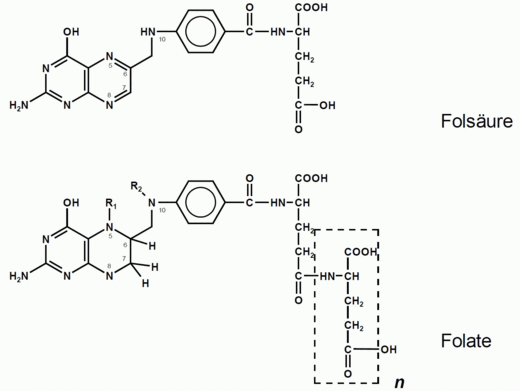
They are derivatives of folic acid (see figure), which is also denominated pteroyl glutamic acid. The latter is a purely artificial compound and usually does not appear as metabolite. The physiologically active forms such as tetrahydrofolic acid are fourfold hydrogenated (see figure). Along with tetrahydrofolate derivatives with one-carbon substituents at N5 and/or N10 occur, of which 5-methyl-, 5-formyl-, 10-formyl, 5,10-methylene- , 5,10-methenyl-, and 5-formimino-H4folate are the most abundant ones.
This so-called pteroyl monoglutamates only play a minor role in foods in comparison with the pteroyl polyglutamates, which may contain n=2 to 7 glutamates.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||